|
Evaluating Software Design Patterns — the "Gang of Four" patterns implemented in Java 6 |
||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
See:
Description
| Interface Summary | |
|---|---|
| SequenceValueGenerator<E> | A sequence value generator can be used as the implementation
for a sequence abstraction as it generates
non-null sequence values that can be delivered by the sequence in
question. |
| Class Summary | |
|---|---|
| Main | Bridge tests. |
| MemorizableSequenceAbstraction<E> | A memorizable sequence abstraction refines a sequence
abstraction so it can save and restore
its internal implementation in form of mementos. |
| SequenceAbstraction<E> | A sequence abstraction defers the creation of
sequence values to a value
generator. |
| SequenceValueArrayList<E extends Serializable> | A sequence value array list stores sequence values
in a java.util.ArrayList instance. |
| SequenceValueCollection<E extends Serializable,C extends Collection<E>> | A sequence value collection is a finite collection of non-null
sequence values that can be used as the implementation for a sequence
abstraction. |
| SequenceValueHashSet<E extends Serializable> | A sequence value hash set stores sequence values
in a java.util.HashSet instance. |
| SequenceValueLinkedHashSet<E extends Serializable> | A sequence value linked hash set stores sequence values
in a java.util.LinkedHashSet instance. |
| SequenceValueRange | A sequence value range generates unique Integer
values within a given range determined at
construction time. |
| SequenceValueSet<E extends Serializable,C extends Set<E>> | A sequence value set stores sequence values in a specific
java.util.Set implementation as specified by the
type parameter C. |
| SequenceValueTreeSet<E extends Serializable> | A sequence value tree set stores sequence values
in a java.util.TreeSet instance. |
| SynchronisedSequenceAbstraction<E> | A synchronised sequence abstraction refines a sequence
abstraction by making it thread-safe. |
| Enum Summary | |
|---|---|
| SequenceValuePolicy | Standard policies for formatting SequenceValueGenerator
objects into char sequences (not part of the core Bridge implementation). |
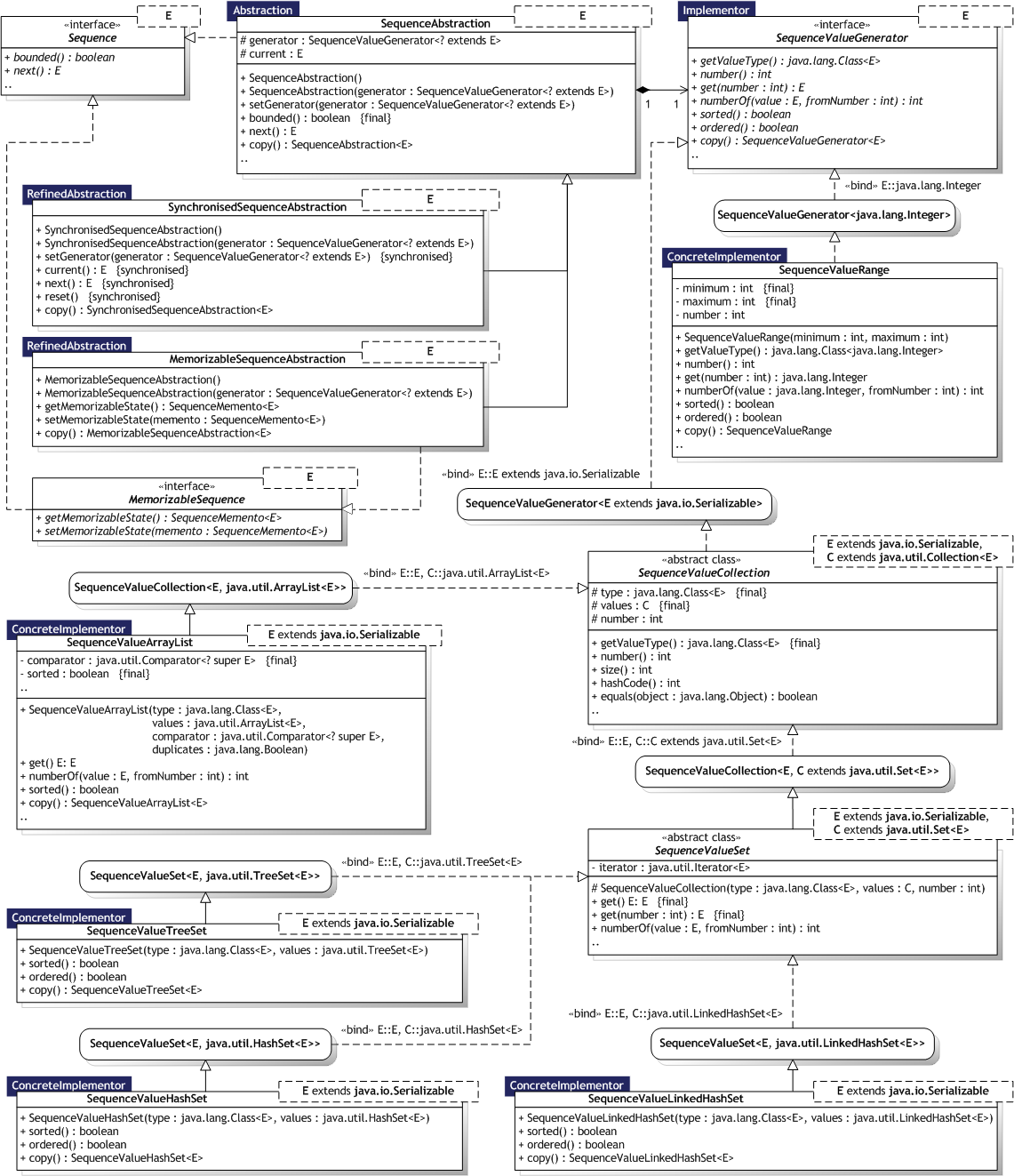
Implementations and examples of the Bridge design pattern [Gamma95, p.151].
Intent:
Decouple an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently.
SequenceAbstraction class,
which allows for abstraction regarding the
Sequence interface.
The RefinedAbstraction participant is represented by
the MemorizableSequenceAbstraction
class.
The Implementor participant is represented by the
SequenceValueGenerator interface,
which defines the functionality needed for all implementors. A
refinement of this interface is the abstract class
SequenceValueCollection, which stores
the actual sequence value delivered by a given sequence abstraction in
a collection. The actual SequenceValueCollection implementations defined
in this package thus represent the ConcreteImplementor participant,
for example the SequenceValueArrayList
and SequenceValueTreeSet classes.
The SequenceValueRange class also
corresponds to the ConcreteImplementor participant, but without
storing the values in a collection.
The size, ordered, and duplicate properties of a SequenceValueGenerator makes it very
easy to alter the behaviour of a given sequence abstraction!
|
Gunni Rode / rode.dk | ||||||||
| PREV PACKAGE NEXT PACKAGE | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||